The World Bank (with financing from the Korea Green Growth Trust Fund) is working to support the Government of India in an effort to stimulate the consideration of enhanced ICT aspects as one aspect of a smart city program. This effort will explore various aspects of ICT use in city planning and management.
See examples of how information collected through various sources (e.g. in-situ sensors or earth observation) can be put together to provide a spatial perspective of cities. Many of the products painstakingly analyzed or compiled by different global and local knowledge providers can be integrated to provide a comprehensive overview of these cities – not only from a local context but from a global context.
Some illustrative visualizations are below:
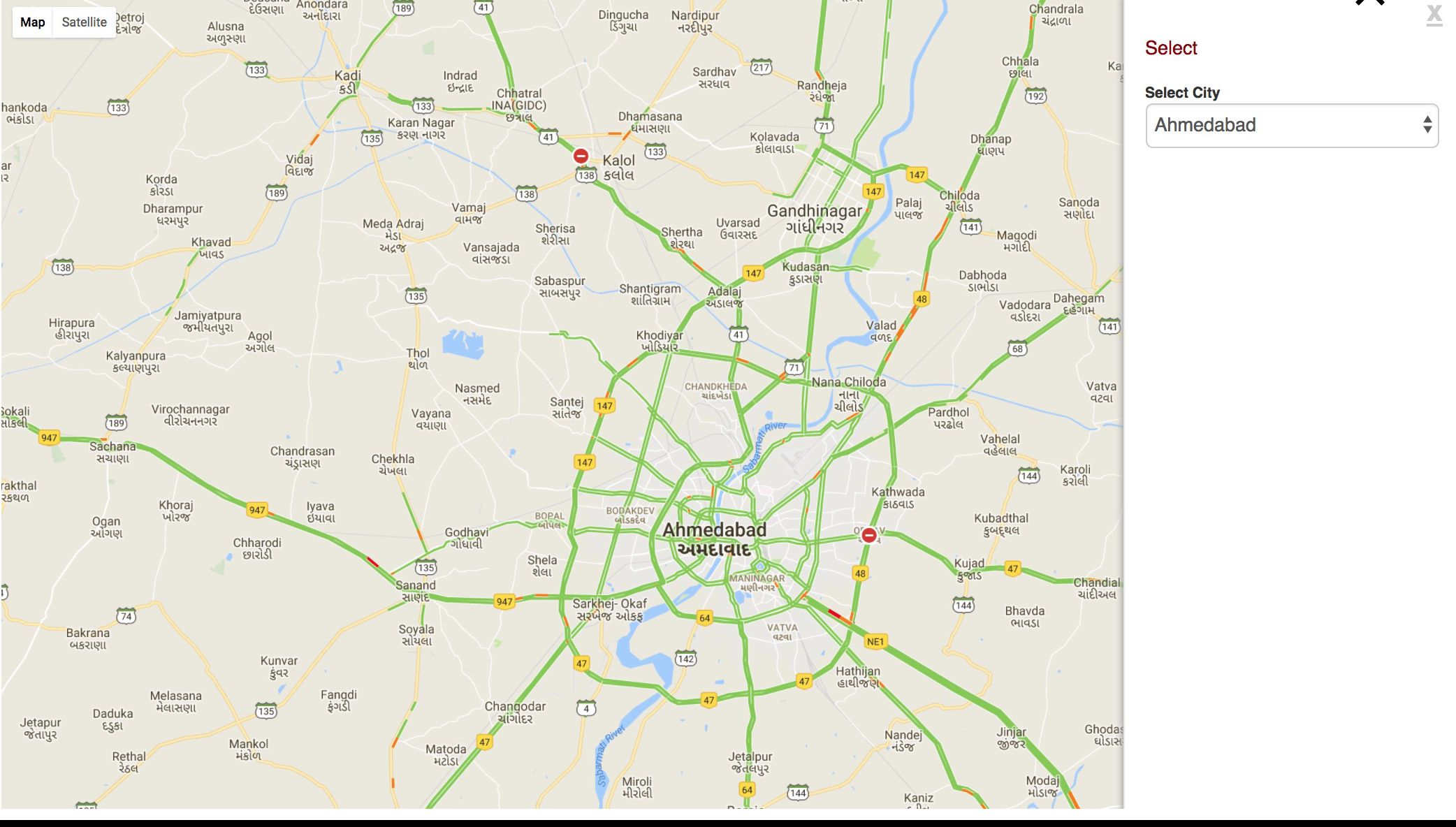
There are a growing number of online resources that provide information on Indian cities that could be useful in the smart city context. Some of these include:
As India makes the journey from villages to towns to cities, there is a need to better embrace these emerging innovations (e.g. in sensors, earth observation, cloud analytics, data visualization/data science, citizen science, IoT, etc.) in order to modernize the way in which cities are developed and managed.


