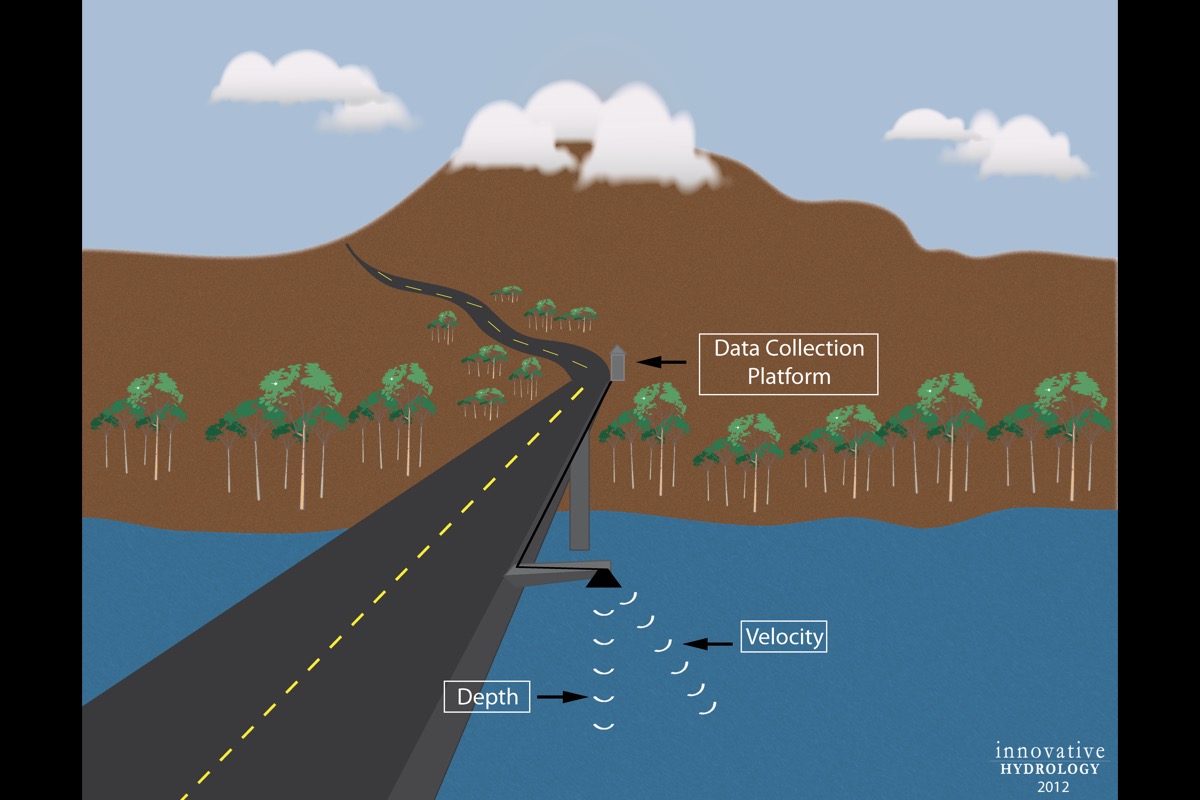
Description: Radar discharge measurement device is a non-contact solution to measure flow. The device generally uses two sensors and assumptions to calculate discharge. One radar/ultrasonic sensor measures the elevation of the water level while the other measures the velocity of water at the surface. The channel profile must be programmed into the devices algorithm so that the discharge approximation can be calculated. As the velocity of water is measured at the surface, an assumption is made of the velocity over the cross section. Assumption is made on the velocity profile, both horizontal and vertical.
The radar discharge is best suited in symmetric channels, such as canals. When used on larger streams or rivers the operator of the device must understand the assumptions of the device makes to determine if the sensor will provide usable measurements. Since the device measures surface water velocity and assumes for the rest of the channel, larger rivers where the radar measurement does not represent flow of the entire channel or where there are multiple channels within the cross section, multiple sensors may be needed. The value of this type of sensor is questionable in water adjudication, as the estimates based on measuring velocity at only on point along the width of the water can be poor, especially with increasing river width. The Radar Discharge sensor can be thought of as an automatic version of the using the float method of discharge. However, the float method generally uses 10 floats or more across a river, while the Radar Discharge sensor only automatically measures a single point. This sensor may be best suited in a situation where horizontal ADCPs are not useful, such as situations where the river banks are very unstable
Costs USD Lower: $10,000
Costs USD Upper: $15,000
Accessories: ACCESSORIES
Advantages: Direct measurement of river discharge
Disadvantages: Generally requires a bridge mount, though some projects have tried to install these sensors from the bank using a boom. The discharge measurement is an approximation, which can produce varying degrees of accuracy based on channel characteristics.
Pictures: